You may be considering migrating your data and information to the cloud for the many security, scalability, and operational benefits it could bring to your organization. But have you considered the costs, time, and steps involved with moving your existing data and systems to the new environment? Understanding how a cloud migration works will help you make a fully informed decision before you begin your cloud journey.
What is a cloud migration?
A cloud migration is the act of moving your organization’s data and information from on-premises or local servers to a remote cloud-based location. Moving to the cloud enables your employees to access information from anywhere at any time. The cloud also brings a host of additional benefits to your organization when implemented correctly.
The first step in your cloud journey is to work with a cloud migration team to understand the goals and objectives of the migration and ensure important factors such as security and governance are considered. They can help you create a migration strategy and a project management plan to ensure you don’t just upgrade your technology — but also achieve your business goals.
It is important to keep in mind that migrating to the cloud may require a larger-than-expected initial investment — and some organizations may be reluctant to pay the costs required to migrate to the cloud. However, the initial investment must be weighed against long-term costs such as upgrading on-premises hardware or employing an onsite team.
Investing in a cloud migration now results in fewer expenses later — and an experienced cloud migration team can help your organization identify opportunities to reduce costs in the future.
Once your cloud migration team has determined how your data will move, you can begin the process of data grouping — which involves organizing your applications, files, and other supporting dependencies as multiple units to enable easier access to all resources.
After the grouping process has been completed, the extract, transform, and load (ETL) process begins, and the team starts migrating the bulk of your data onto the cloud instance.
Here’s how that works:
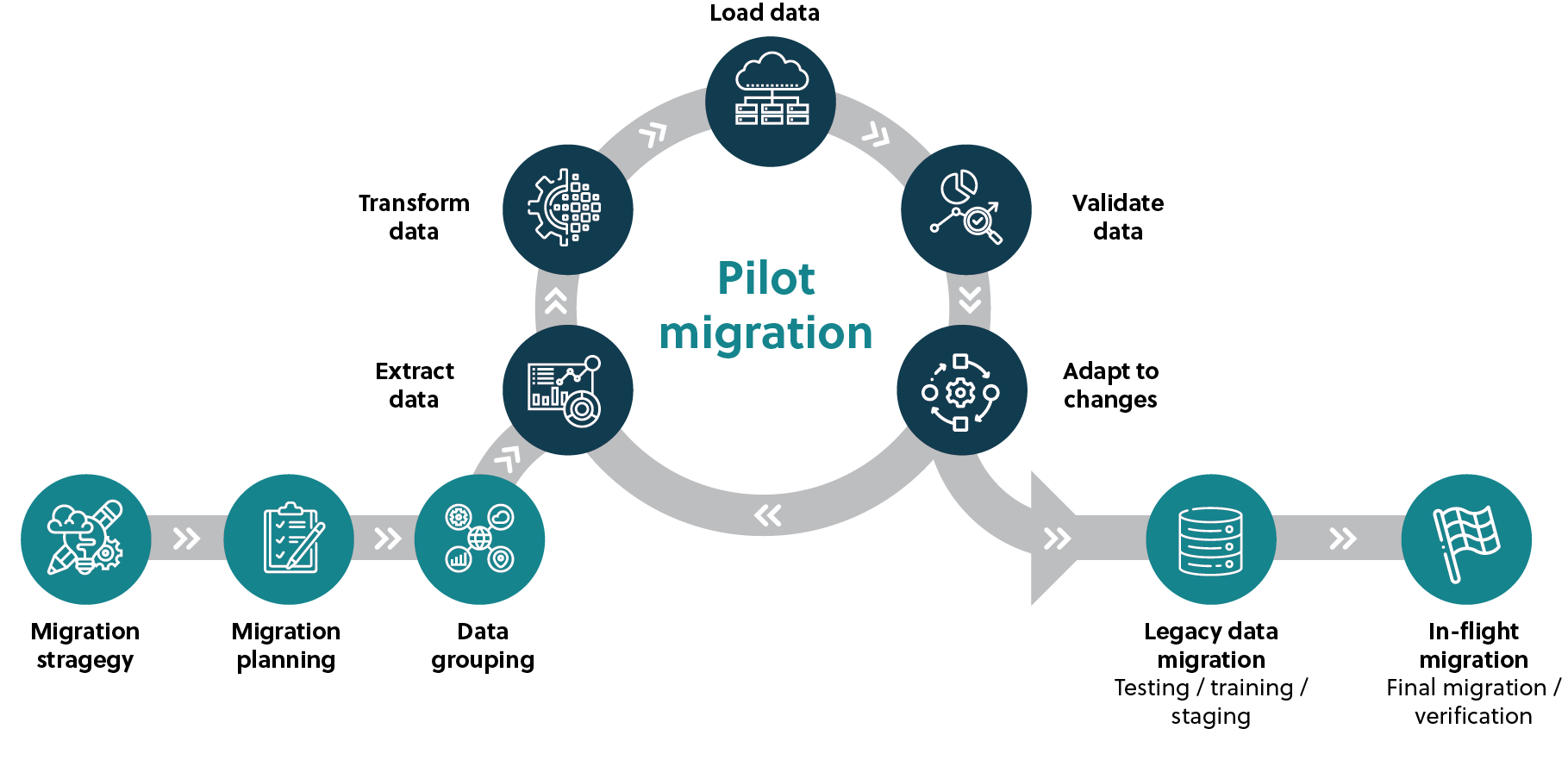
While this is one approach, there are several different ways to complete a cloud migration depending on your data architecture. Additionally, data volume may have an impact on which approach works best for you. For example, an organization with a large amount of on-premises data may want to use Azure Data Box to complete a one-time data load, or lift and shift, to the cloud.
Extract
Extracting data from a pile of information is one of the most critical steps in the data migration process. Typically, information comes from various systems — including customer relationship management systems, data servers, spreadsheets, and other legacy databases.
A streamlined ETL process should preserve all your data during the migration, including reports, accounts, workflows, dashboards, etc. that you have stored on your network. Your migration team can demonstrate the steps they take to ensure this happens.
Transform
Many file types, workflows, and information are not readily usable by all cloud platforms, and therefore it is crucial to transform your data into the correct formats so that it is ready to upload. Standardizing, deduplicating, and verifying occur during the transform portion of the migration to ensure the data is compatible with the cloud.
Data scrubbing and data cleansing also occur during the transform process. For a successful migration, the target system (the new cloud instance) must receive accurate data from the source system. The transform process is critical to ensure data integrity between the source system and the target system.
It is best practice for data transformations to occur as close to the source as possible. For example, data cleansing should ideally take place in the source system itself, rather than the target system. However, the data owners ultimately decide how the data is transformed into the instance.
Load
During this portion of the migration, your migration team will inspect the data and adapt it as necessary to smooth the migration process. The ETL process repeats until all the data is validated and adapted for the cloud.
The process will typically require multiple ETL iterations to migrate all legacy onto the cloud instance. A final in-flight migration follows to close all loops, and verify that all your data is present, and no key information is missing that could cause data linkage issues.
What are the benefits of the cloud?
The cloud is an essential tool to support collaboration and operational agility as hybrid and remote workplaces continue to grow in popularity. Moving to the cloud helps your organization ensure your data is safe and secure while being easily accessible to members of your organization from any place and at any time.
Some of the benefits your organization could gain from a cloud migration include:
The cloud is scalable, flexible, and upgradable
Cloud solutions enable your organization to implement multiple programs within a single cloud instance. By shifting to cloud solutions, you ensure your organization can incorporate pre-existing infrastructure within a new virtual environment, where costs are lower than maintaining expensive data centres.
Cloud servers also allow for quicker growth and customization to meet your organization’s future needs. According to a survey by Microsoft, almost 82 percent of small businesses using cloud solutions noticed a significant decrease in costs following a migration.
Increased security
According to a 2016 survey, 94 percent of businesses who converted to cloud-based solutions reported security benefits since moving to an online instance. Cloud services receive frequent updates and come equipped with tough firewalls to protect information from unwarranted users. Cloud services generally maintain data in a more secure fashion than on-premises solutions.
Most cloud platforms also use role-based authentication to ensure data protection and privacy. Using various encryption methods, information is housed in an environment that is customized to allow user privileges.
Microsoft Azure specifically uses three different security protocols: role-based security, record-based security, and field-based security.
Role-based security ensures that various members of an organization can each have specific data access permissions. Administrators control this access and can change access levels as required.
Similarly, record-based security establishes which users have access to your organization’s records and what they can do with this information. Moreover, there may be cases where certain fields within an entity contain sensitive data that should not be viewed by all members of your organization. For those instances, field-based security allows administrators to control user access to specific data fields.
Key considerations for your cloud migration
It is essential to work with an experienced team of cloud migration experts if you are considering migrating your organization’s data and information to the cloud. A cloud migration team can provide you with the knowledge to identify the challenges you may encounter during your organization’s cloud transformation and potential solutions, including:
- Selecting the right technology — A team of cloud migration experts can help identify the cloud infrastructure that best fits the needs of your business and deploy technology in a way that aligns with your high-level strategy and existing timelines.
- Creating a cloud strategy — There are a host of different systems and strategies within the cloud computing landscape. A team of cloud migration experts can provide you with the knowledge to decide what data remains onsite if you choose a hybrid cloud solution or to determine who will manage your applications after your cloud migration is complete. Additionally, a team of cloud migration experts can help create a customized cloud plan for security and governance to suit the needs of organizations with varying sizes and budgets.
- Cost optimization — While migrating to the cloud has the potential to be expensive initially, a cloud migration team can help find the solution that best fits your budget and estimate your return on investment. It’s also important that you are only paying for what you need, and a cloud migration team will help ensure you don’t encounter any surprises when you begin to see your consumption and storage costs after the migration is complete.
Connect with us to get started
Our team of dedicated professionals can help you determine which options are best for you and how adopting these kinds of solutions could transform the way your organization works. For more information, and for extra support along the way, contact our team.
